Epistaxis: A complete guide
What is epistaxis
Epistaxis, also called as a nosebleed, occurs when there is bleeding from the nose. It is a very common complaint. Although it is not a life-threatening condition, but becomes a matter of concern for the parents of kids. Generally, the nosebleeds are self-limiting ,benign and spontaneous, but in some cases, it can be recurrent. Epistaxis is a very common disease. Most of the people must have faced nose bleeding once in their lifetime. It is most common among the age group of 2 to 10 and 45 to 80 years. Both males and females are affected equally. Children with migraine problem are more prone to recurrent epistaxis.

What is epistaxis
Type of epistaxis
Epistaxis can be categorized into two types on the basis of sites from which bleeding occurs.
1. Anterior nose bleeding- This is a common form.
2. Posterior nose bleeding- This type is not common.
Other than anterior and posterior sites bleeding may rarely also reach the nasolacrimal duct and come out of the eyes. Nausea &vomiting may also occur if the clotted and fresh blood flows down into the stomach.
What are the causes of epistaxis
Epistaxis can be caused due to local causes, systemic causes, and idiopathic causes.
Local cause includes
- Trauma- Most common cause of Epistaxis is local trauma. Although facial trauma, nasal infection, sinus infections, foreign bodies and intake of non humid air for a long time contribute to the less common cause. In children, trauma is caused by repeated picking of nasal septum due to bleeding and ulceration of mucous of anterior septum.
- Trauma can also be caused due to foreign bodies like naso-tracheal and nasogastric tubes. Other than this facial & nasal trauma also cause Epistaxis.
- Dry weather- Less humid air can cause irritation to the mucosa.

causes of epistaxis
- Drugs- Application of Corticosteroids and antihistamines typically causes mucosal irritation. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can also cause bleeding from the nose.
- Septal abnormality- DNS ( septal deviations)/ spurs cause disturbance in the normal airflow in the nose which causes dryness in the nasal mucosa.
- Inflammation- Mucosal inflammation can be caused due to bacterial, allergic rhinosinusitis and viral infections. Bleeding is in the form of blood streaked discharge from the nose. In neonates, there may be bleeding from the nose secondary to gastroesophageal reflux due to inflammation.
- Tumors- Malignant and benign tumors can cause epistaxis. There may sign of nasal blockage and unilateral rhinosinusitis. Juvenile angiofibroma of the nose, intranasal rhabdomyosarcoma also manifests epistaxis.
- Blood dyscrasias- congenital coagulopathies that are hereditary is associated with easy bruising, bleeding for a long time from a minor wound or surgery.
Local cause includes
- Acquired coagulopathies like thrombocytopenia, liver disease in which there is a lower level of coagulation factors.
- Women on oral contraceptives, alcoholics are also prone to epistaxis.
- Vascular abnormalities- Arteriosclerotic disease of blood vessels is a cause of epistaxis in old people. In this disease, there is a deficiency of muscular or vascular tissue in the walls of vessels. So even a minor trauma can cause bleeding that doesn’t stop spontaneously.
- A migraine- kids who have migraine headaches are more prone to epistaxis than the kids who don’t have this problem.
- Hypertension- Hypertension causes vascular fragility due to a prolonged period of the disease. So there may be nasal bleeding in hypertensive patients. Controlling epistaxis in hypertensive patients is a bit difficult, especially for patients with high systolic blood pressure. Idiopathic causes- cause for epistaxis is unknown in approximately 10% of the population.
Investigation of epistaxis
- First of all patients, medical history is analyzed.
- Patient should be interrogated about trauma
- Family history of hypertension or any clotting disorder should be ruled out
- Ask the patient if he has gone any surgery in nose previously
- Ask about the drugs that patient is taking like aspirin
- Most of the time investigations are not required except recurrent epistaxis. In recurrent epistaxis, investigation should be done to rule out an underlying disease
- Blood typing, coagulation studies, the FBC can be done in severe cases
- Suspected nasal malignancy should be referred to the specialist.
- CT scan / Naso pharyngoscopy can be done
How is epistaxis managed
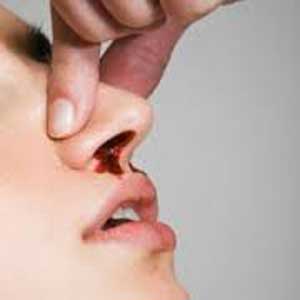
Management requires packing, cauterization, or balloon devices. First aid treatment for epistaxis include following steps:
- Pressure your nose with the fingers for at least 5 to 10 minutes
- Apply cold compress over the nose
- Take deep breaths.
- Apply topical vasoconstrictor.
How is epistaxis managed
Preventive measures to prevent epistaxis
- Use saline nasal spray to keep the nasal mucosa moist.
- Avoid blowing nose too hard.
- Do not sneeze with an open mouth.
- Do not manipulate your nose with your fingers.
- Avoid spicy and hot foods.
- Avoid taking a hot shower
- Avoid NSAIDs and aspirin.
- Epistaxis is rarely a life-threatening condition. Mortality associated with epistaxis is rare. When epistaxis is treated with adequate care chances of rebleeding is rare.

Preventive measures to prevent epistaxis














































